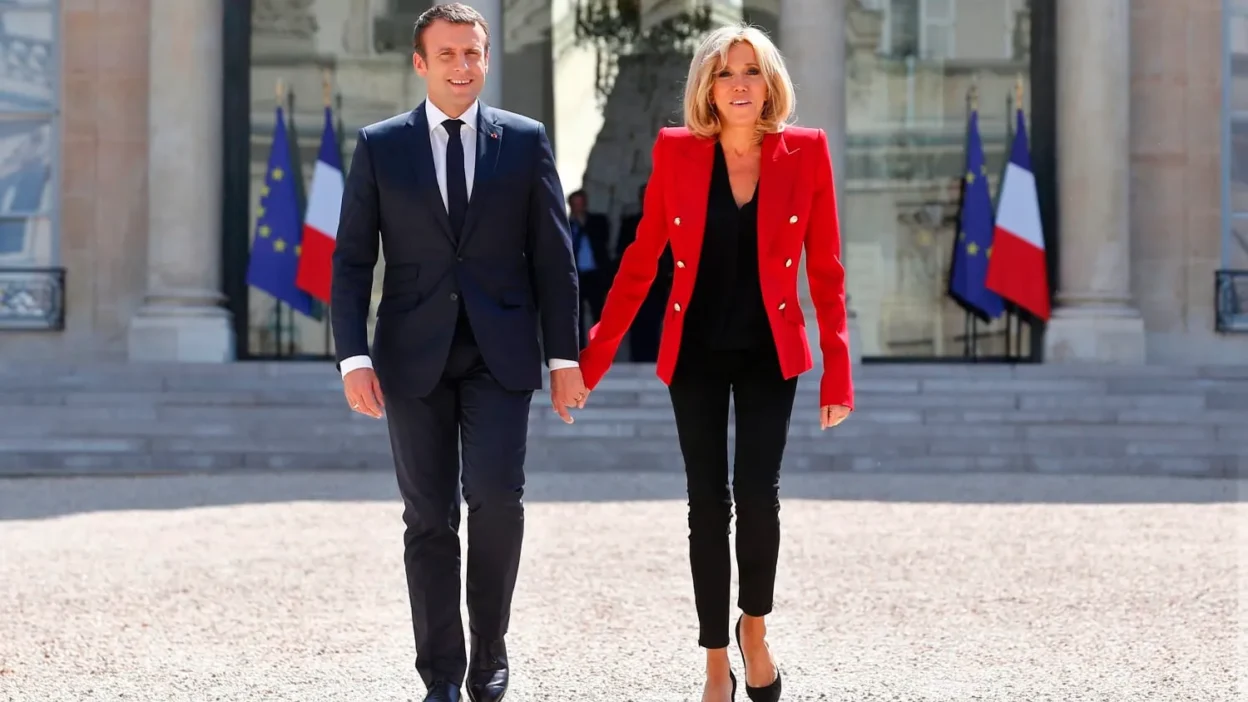
As the wife of French President Emmanuel Macron, Brigitte Macron has become one of the most discussed political spouses in the world.
While the role of First Lady in France carries no official constitutional power, it often attracts intense public and media attention—something Brigitte Macron has experienced since her husband’s rise to the presidency in 2017.
Much of the fascination surrounding her centers on her background, her unconventional path to the Élysée Palace, and the way she challenges traditional expectations of political spouses.
Beyond headlines and online debate, Brigitte Macron is a former educator, a public advocate for social causes, and a visible figure in modern French public life.
Her presence has sparked conversations about age, gender norms, privacy, and the evolving role of women in politics.
This article takes an in-depth look at who Brigitte Macron really is—exploring her life, career, public initiatives, and the broader cultural context that shapes how she is perceived both in France and internationally.
Early Life and Family Background
Brigitte Macron was born Brigitte Marie-Claude Trogneux on April 13, 1953, in Amiens, a city in northern France with a strong cultural and commercial heritage. She grew up in a well-known local family; the Trogneux name is associated with a successful chocolate and confectionery business that has operated in the region for generations. Raised in a comfortable, traditional environment, she was the youngest of six children, which shaped her early sense of independence and resilience.
From a young age, Brigitte showed a strong interest in literature, language, and the arts. Her upbringing emphasized education, discipline, and cultural refinement—values that would later define both her professional career and public demeanor. She pursued higher education in the humanities, focusing on French literature and Latin, subjects that reflected her deep appreciation for classical learning and intellectual rigor.
Amiens itself played an important role in shaping her worldview. As a city that blends tradition with modernity, it provided an environment where cultural life, education, and civic engagement were closely connected. This background helped foster her later commitment to education and social causes.
Before entering public life, Brigitte lived largely outside the political spotlight, building a family and professional identity rooted in teaching rather than ambition for public recognition. Her early life reflects a blend of bourgeois stability, intellectual curiosity, and cultural engagement, elements that continue to influence how she presents herself today as France’s First Lady.
Career as an Educator
Before becoming a public figure, Brigitte Macron built a long and respected career in education, which remains a defining part of her identity. Trained in French literature and classical languages, she worked as a secondary school teacher, specializing in French literature and Latin. Teaching was not simply a profession for her but a vocation rooted in intellectual exchange, discipline, and mentorship.
She taught at several well-regarded institutions, including schools in Amiens and later in Paris, where she became known for her rigorous academic standards and close engagement with students. Colleagues and former pupils have often described her as demanding yet deeply committed, encouraging critical thinking, confidence in expression, and a strong appreciation for literature and theater. She was also actively involved in drama and extracurricular cultural activities, using the arts as a tool for education and personal development.
Brigitte Macron’s years in the classroom shaped many of the skills that later became visible in her public role. Her ability to communicate clearly, engage diverse audiences, and convey complex ideas with precision can be traced directly to her teaching background. This experience also informed her strong advocacy for education-related causes once she entered public life.
Even after assuming the informal role of First Lady, she has continued to emphasize the importance of education, particularly in areas such as school bullying, youth development, and access to learning opportunities. Her career as an educator provides important context for understanding her priorities, her public initiatives, and the values she brings to her role alongside the French president.
Meeting Emmanuel Macron: Context and Timeline
Brigitte Macron’s relationship with Emmanuel Macron is one of the most closely examined aspects of her life, largely because it diverges from conventional expectations of political couples. The two first met in the early 1990s in Amiens, where Brigitte was working as a teacher and Emmanuel Macron was a student involved in a school theater program. Their initial connection developed through shared interests in literature, theater, and intellectual discussion, forming a bond rooted in cultural and academic exchange.
As time passed, their relationship evolved under complex personal and social circumstances. Brigitte Macron was married at the time and had a family, while Emmanuel Macron pursued his education away from Amiens. Their paths separated for several years, during which both followed independent personal and professional journeys. It was only later, when Emmanuel Macron had reached adulthood and established himself academically and professionally, that their relationship resumed.
The progression of their partnership required navigating public scrutiny and private challenges, particularly given the unconventional nature of their age difference. Both have spoken about the emotional difficulty of this period, emphasizing the importance of mutual respect, autonomy, and patience in their decision to be together.
They married in 2007, long before Emmanuel Macron entered frontline politics, at a time when he was building his career in public administration and finance. Understanding the full context and timeline of their relationship is essential, as it helps separate fact from speculation and provides a clearer picture of a partnership shaped over many years rather than by political ambition.
Marriage and Personal Life
Brigitte and Emmanuel Macron were married in October 2007 in Le Touquet, a seaside town in northern France that holds personal significance for them. At the time of their marriage, Emmanuel Macron was still far from national political prominence, and their life together unfolded largely outside public attention. This period allowed them to establish their partnership away from the intense scrutiny that would later accompany his political career.
Brigitte Macron has three children from her previous marriage and is also a grandmother, a role she has spoken about with warmth and pride. Family remains an important part of her life, though she has consistently sought to protect her children and grandchildren from media exposure. This careful balance between public visibility and private boundaries has been a recurring theme throughout her time in the spotlight.
The Macrons often describe their relationship as a partnership built on mutual support and intellectual exchange. Emmanuel Macron has publicly acknowledged his wife’s influence on his confidence, communication style, and emotional resilience, particularly during demanding political moments. Despite their high-profile status, they have made deliberate efforts to maintain routines and moments of normalcy, including shared cultural interests such as reading, theater, and music.
As Emmanuel Macron’s political responsibilities expanded, Brigitte Macron’s role naturally became more public. However, she has continued to emphasize that her private life is not defined solely by her husband’s position. Their marriage, formed long before the presidency, is frequently presented by both as a personal commitment first and a public partnership second—an important distinction that helps explain their approach to public life and shared visibility.
The Age Difference: Media Coverage and Public Debate
One of the most frequently discussed aspects of Brigitte Macron’s public image is the age difference between her and President Emmanuel Macron. This element of their relationship has attracted sustained media attention, often overshadowing her professional background and public initiatives. While age gaps in relationships are not uncommon, the visibility of the French presidency has amplified scrutiny and debate, particularly in international media.
Coverage of the age difference has frequently revealed gender-based double standards. Comparisons are often made to relationships in which older male leaders have younger partners—situations that historically receive far less criticism. In contrast, Brigitte Macron’s role has prompted discussions about societal expectations of women, power dynamics, and public acceptability. These conversations vary widely depending on cultural context, with reactions differing notably between French and non-French audiences.
In France, public discourse has generally been more restrained, with greater emphasis placed on personal autonomy and privacy. However, online platforms and tabloid media have contributed to the spread of speculation and exaggerated narratives. Brigitte Macron has addressed this attention indirectly, expressing that while public criticism can be difficult, she refuses to let it define her identity or her role.
Importantly, both Brigitte and Emmanuel Macron have consistently framed their relationship as one based on consent, maturity, and long-term commitment. Over time, the intensity of the debate has lessened as her work as First Lady has become more visible. Still, the focus on age difference remains a telling example of how public figures—especially women—are often judged through personal lenses rather than professional contributions.
Becoming First Lady of France
When Emmanuel Macron was elected President of France in May 2017, Brigitte Macron entered one of the most visible yet loosely defined roles in French public life. Unlike in some countries, the position of First Lady of France has no official constitutional status, salary, or formal powers. Nevertheless, the spouse of the president plays a significant symbolic and social role, representing the country alongside the head of state.
Brigitte Macron’s arrival at the Élysée Palace marked a shift in how the role was perceived and discussed. Early in Emmanuel Macron’s presidency, public debate emerged around transparency and expectations, leading to the publication of a formal charter outlining the First Lady’s responsibilities. This document clarified that her role would focus on representation, social and cultural initiatives, and public engagement, while remaining unpaid and non-political.
As First Lady, Brigitte Macron became a highly visible presence at official ceremonies, international state visits, and national commemorations. Her background as an educator influenced her approach, favoring direct engagement, listening, and advocacy over ceremonial distance. She quickly established herself as an active participant rather than a passive figure, while still respecting the institutional boundaries of the role.
Her position also came with heightened scrutiny, particularly regarding legitimacy and influence. Brigitte Macron has consistently emphasized that she does not seek political authority but aims to use her visibility to support social causes. Becoming First Lady transformed her private life irrevocably, placing her at the intersection of public service, representation, and personal identity in modern French politics.
Official Role and Public Initiatives
As First Lady, Brigitte Macron has focused much of her public activity on social and educational initiatives, areas closely aligned with her professional background. While the role carries no legislative power, it provides a platform to highlight issues that may otherwise receive limited national attention. From the beginning of her tenure, she made it clear that her involvement would be centered on practical engagement rather than political advocacy.
One of her most visible areas of work has been education and youth welfare, particularly the fight against school bullying. She has supported national awareness campaigns, worked with educators and associations, and participated in initiatives aimed at prevention, early intervention, and support for affected families. Her experience as a teacher has lent credibility to her efforts and shaped her hands-on approach.
Brigitte Macron has also been involved in initiatives supporting people with disabilities, health-related causes, and social inclusion. She regularly meets with charities, non-profit organizations, and community groups, using her position to amplify their work and encourage collaboration with public institutions. These engagements often take place behind the scenes, reflecting her preference for substance over publicity.
In addition to domestic causes, she represents France internationally during state visits, where she engages in cultural and humanitarian exchanges with counterparts abroad. Throughout her tenure, Brigitte Macron has emphasized continuity and long-term impact rather than short-term visibility. Her public initiatives illustrate how the First Lady’s role, though informal, can serve as a meaningful channel for social advocacy when grounded in personal expertise and sustained commitment.
Political Influence and Advisory Role
Although Brigitte Macron holds no elected office and has no formal political authority, her proximity to the president has naturally led to public discussion about her influence and advisory role. In France, it is not uncommon for presidential spouses to act as trusted confidants, offering personal advice rather than participating directly in policymaking. Brigitte Macron’s role fits within this long-standing tradition, though heightened media attention has made it more visible.
Emmanuel Macron has openly acknowledged that his wife is one of his closest advisors, particularly when it comes to communication, tone, and public perception. With her background in literature and teaching, she is said to provide feedback on speeches, messaging, and interpersonal dynamics, helping refine clarity and emotional resonance. This form of influence is informal and personal, distinct from institutional political power.
Critics have occasionally questioned the transparency of such influence, especially during moments of political tension. In response, the Élysée has consistently emphasized that Brigitte Macron does not participate in government meetings, policy formulation, or decision-making processes. Her input remains private and advisory, comparable to that of a spouse rather than a political actor.
Supporters argue that her role highlights the human dimension of leadership, offering emotional support and perspective in an otherwise highly strategic environment. More broadly, the debate surrounding her influence reflects larger questions about accountability, trust, and the boundaries between personal relationships and public office. Brigitte Macron’s advisory presence underscores how modern leadership often involves unseen networks of support, even when official power rests firmly within formal institutions.
Fashion, Public Image, and Media Representation
Brigitte Macron’s public image has been shaped not only by her role as First Lady but also by intense media attention to her appearance, fashion choices, and personal style. From the beginning of Emmanuel Macron’s presidency, international press outlets frequently highlighted her wardrobe, often positioning her as a modern and unconventional figure among global political spouses. This focus reflects broader trends in how women in public life are visually scrutinized to a far greater extent than their male counterparts.
Her style is often described as minimalist, contemporary, and distinctly French, favoring clean lines, tailored silhouettes, and neutral colors. French media has generally framed her fashion choices as an extension of national elegance and modernity, while international outlets have sometimes treated them as symbols of cultural difference or novelty. Supporters argue that her presentation reinforces confidence and authority, while critics question why appearance receives such disproportionate attention compared to substance.
Beyond fashion, Brigitte Macron’s public image is closely managed, balancing accessibility with dignity. She is frequently portrayed as warm and approachable during public engagements, particularly when interacting with children, educators, and community groups. At the same time, she has maintained firm boundaries regarding privacy, especially concerning her family.
Media representation of Brigitte Macron varies significantly by platform and country. Traditional French journalism tends to emphasize her initiatives and public role, whereas tabloid and social media environments often amplify controversy and personal commentary. This contrast highlights the challenges faced by high-profile women navigating visibility, expectation, and representation in the digital age, where image can sometimes eclipse action.
Criticism, Controversies, and Misinformation
Like many prominent public figures, Brigitte Macron has faced criticism and controversy, much of it amplified by the speed and reach of digital media. While some scrutiny is an expected consequence of public life, she has also been the target of persistent misinformation and false narratives, particularly on social media platforms. These claims have often focused on her personal life rather than her public work, reflecting a broader pattern of gendered attacks against women in visible positions.
Several conspiracy theories and defamatory rumors have circulated online, gaining traction beyond France and reaching international audiences. In response, Brigitte Macron has taken legal action in certain cases to challenge false statements and protect her reputation. These actions underline the seriousness of misinformation and its potential harm, not only to individuals but also to public discourse more broadly.
Criticism has also emerged regarding the visibility and perceived influence of the First Lady’s role. Some critics question the level of attention devoted to a position without formal authority, while others argue that her public engagements blur the line between representation and political involvement. Supporters counter that her work remains transparent, non-partisan, and focused on social issues rather than policy.
The controversies surrounding Brigitte Macron illustrate how misinformation thrives in polarized and highly connected environments. They also highlight the challenges faced by public figures in correcting falsehoods once they spread. Her experience has become a case study in the impact of digital rumor, the limits of privacy, and the importance of responsible media practices in democratic societies.
Public Perception in France and Abroad
Public perception of Brigitte Macron varies significantly between France and the international community, shaped by cultural norms, media framing, and differing expectations of political spouses. Within France, opinions about her are generally more measured. While she remains a visible and sometimes polarizing figure, many French citizens view her primarily through the lens of her public initiatives and her support role alongside the president rather than focusing solely on her personal life.
French media coverage tends to be relatively restrained, often emphasizing her work in education, social inclusion, and representation at official events. Over time, familiarity has reduced some of the initial controversy surrounding her presence at the Élysée Palace. Polls and public commentary suggest that while she is not universally admired, she is broadly accepted as part of the contemporary presidential landscape.
Abroad, particularly in Anglo-American and tabloid-driven media, Brigitte Macron’s image is often framed more sensationally. International coverage has frequently focused on her relationship with Emmanuel Macron, highlighting elements perceived as unconventional. This difference in tone reflects contrasting cultural attitudes toward age, gender roles, and the visibility of political spouses.
Despite this divergence, Brigitte Macron is also recognized internationally as a symbol of modern French identity, often associated with elegance, confidence, and social engagement. Her interactions with other world leaders’ spouses during state visits contribute to France’s soft power and diplomatic image.
Overall, the contrast between domestic and international perception underscores how public figures can be interpreted differently depending on cultural context, media priorities, and societal expectations, revealing as much about audiences as about Brigitte Macron herself.
Brigitte Macron as a Symbol in Modern France
Over time, Brigitte Macron has come to represent more than the traditional role of a president’s spouse; she has become a symbol of social change and modernity in France. Her presence at the Élysée Palace challenges long-standing assumptions about age, gender roles, and how women are expected to appear and behave in public life. Rather than conforming to a conventional or purely ceremonial model, she embodies a version of visibility shaped by experience, confidence, and personal history.
In a society that values intellectualism and cultural engagement, Brigitte Macron’s background as an educator resonates with broader French ideals. Her emphasis on education, dialogue, and civic responsibility reflects a belief that influence does not require formal authority. For many supporters, she represents a break from rigid expectations placed on women, particularly older women, in positions of prominence.
At the same time, her symbolic role has sparked debate. Critics argue that her visibility exposes unresolved tensions in French society regarding power, privilege, and representation. These discussions, while sometimes contentious, have contributed to wider conversations about inclusivity, respect, and evolving social norms. In this sense, Brigitte Macron functions as a cultural mirror, reflecting both progress and resistance within contemporary France.
Internationally, she is often seen as emblematic of a modern French presidency—self-assured, unconventional, and media-savvy. Domestically, her symbolism is more nuanced, shaped by history, tradition, and political context. Ultimately, Brigitte Macron’s significance lies not only in what she does, but in what her presence signifies: a France negotiating change while redefining the boundaries of public life and personal identity.
Legacy and Long-Term Impact
As Emmanuel Macron’s presidency progresses, discussions around Brigitte Macron’s legacy increasingly focus on how she has reshaped expectations of the First Lady’s role in France. Although the position remains unofficial and unpaid, her visibility and sustained engagement have left a lasting mark on how the role is understood by the public and the media. She has helped normalize a more active, hands-on approach centered on social issues rather than purely ceremonial duties.
One of the most significant aspects of her long-term impact lies in education and youth advocacy. Her emphasis on anti-bullying initiatives, support for vulnerable students, and engagement with educators has brought renewed attention to issues that resonate beyond political cycles. Even without legislative power, her consistent presence has helped keep these topics part of the national conversation.
Brigitte Macron has also influenced broader cultural perceptions. By remaining visible, confident, and professionally grounded later in life, she has challenged ageist assumptions and expanded representations of women in public roles. This cultural impact may outlast specific initiatives, contributing to more inclusive views of leadership, partnership, and public service.
Critically, her tenure has clarified boundaries around transparency and accountability for presidential spouses, setting precedents that future administrations are likely to follow. The publication of a role charter, increased media scrutiny, and clearer expectations all form part of her institutional legacy.
Ultimately, Brigitte Macron’s long-term impact is not defined by policy outcomes but by symbolic and social influence. Her legacy will likely be remembered as one that modernized the image of the First Lady—making it more engaged, more human, and more reflective of contemporary French society.
Frequently Asked Questions About Brigitte Macron
Who is Emmanuel Macron’s wife?
Emmanuel Macron’s wife is Brigitte Macron, née Brigitte Trogneux. She has been the First Lady of France since 2017 and is a former French literature and Latin teacher.
How old is Brigitte Macron?
Brigitte Macron was born on April 13, 1953. Her age has often been discussed in the media, though she has consistently emphasized that her public work matters more than personal details.
What is the age difference between Macron and his wife?
There is an age gap of 24 years between Brigitte Macron and Emmanuel Macron. This aspect of their relationship has drawn significant attention and sparked debate, particularly outside France.
When did Brigitte and Emmanuel Macron get married?
They were married in 2007, a decade before Emmanuel Macron became president. Their marriage took place long before national political ambitions brought them into the public spotlight.
Does Brigitte Macron have children?
Yes. Brigitte Macron has three children from a previous marriage and is also a grandmother. She keeps her family life largely private.
What does Brigitte Macron do as First Lady?
Although the role is unofficial, she focuses on education, anti-bullying initiatives, disability advocacy, and social inclusion. She also represents France during official events and state visits.
Is Brigitte Macron involved in politics?
She does not hold political office or participate in policymaking. Her role is advisory and representational, offering personal support to the president rather than political authority.
Why is Brigitte Macron so well known internationally?
Beyond her position as First Lady, international attention has been driven by media focus on her background, relationship with the president, and her visible, modern approach to the role.
Conclusion:
Brigitte Macron’s public identity is often reduced to a single label—“Macron’s wife”—yet such a description captures only a fraction of who she is and the role she plays in contemporary France.
Over the years, she has emerged as a complex public figure shaped by her background as an educator, her visibility as First Lady, and her resilience in the face of intense scrutiny.
Her life story reflects personal conviction, intellectual engagement, and a sustained commitment to social causes rather than a pursuit of political power.
Throughout Emmanuel Macron’s presidency, Brigitte Macron has navigated a delicate balance between representation and restraint.
Without holding formal authority, she has nonetheless used her platform to draw attention to education, youth welfare, disability inclusion, and civic dialogue.
Her approach demonstrates how influence can exist outside institutional frameworks, grounded instead in experience and consistency.
The public debates surrounding her—whether focused on age, gender norms, or visibility—also reveal broader societal tensions about women in public life.
In this sense, her story is not only personal but cultural, illustrating how expectations continue to evolve in modern democracies.
Ultimately, Brigitte Macron’s significance lies in moving beyond superficial narratives.
Seen in full context, she is not merely the spouse of a political leader but a figure who has contributed to redefining the modern role of the First Lady.
Her story invites a more thoughtful conversation about partnership, visibility, and respect in public life.

I’m Stephen King, and on WildPickUpLines.com, I share my best pick up lines to make you smile and impress anyone.
Join me to discover funny, flirty, and creative lines that work every time!